VOCAL provides developers a comprehensive suite of embedded software modules optimized for DSPs and available for a range of platforms. Our software modules may be licensed individually or as a library. Custom solutions are also available to meet your unique application requirements. Contact us to discuss your application requirements and licensing needs.
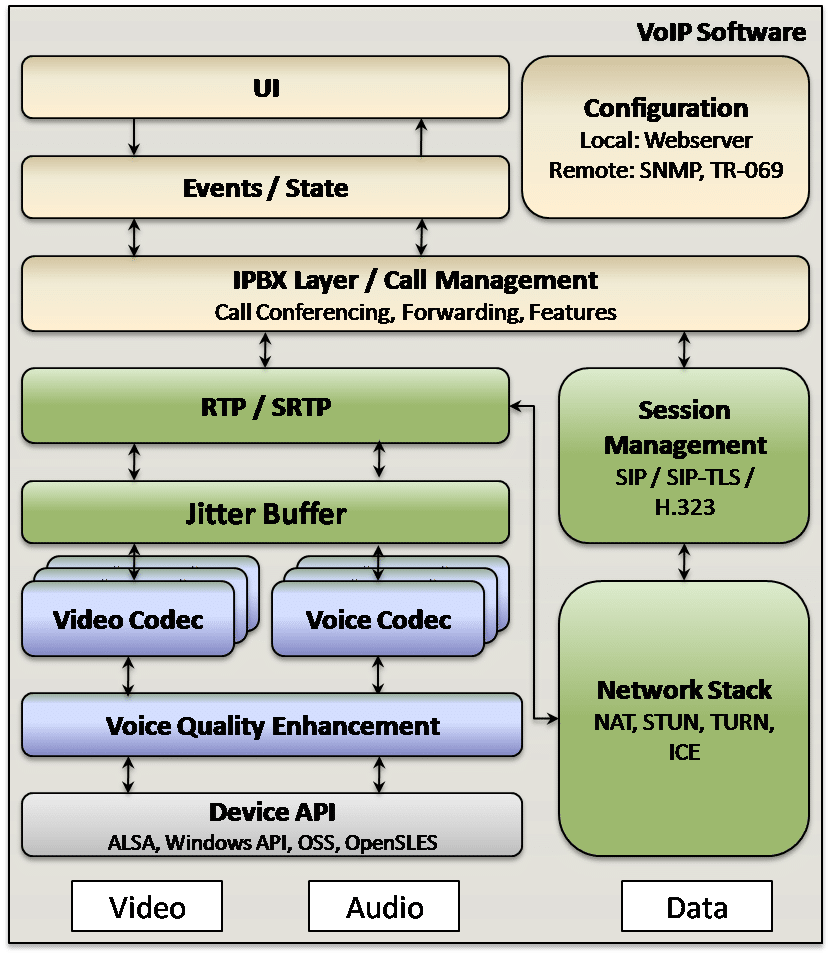
VoIP
V2oIP
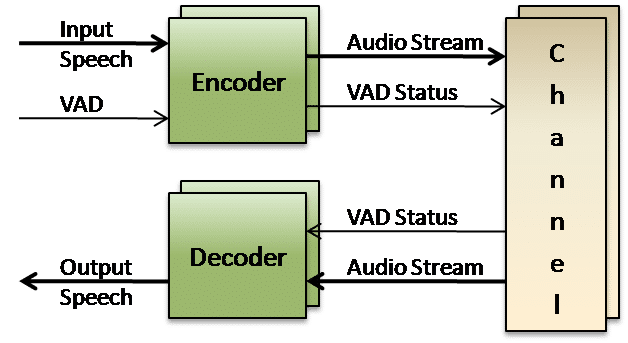
Voice Codecs
- Overview
- Voice Over Network Framework – RTP Packetization, AAL2 Framing
- ITU Speech Coders
- ITU G.711 – 64k bps PCM (A-law or μ-law form)
- ITU G.722 – 7 kHz audio coding within 64 kbit/s (SB-ADPCM)
- ITU G.722.1 – 24k and 32k bps 7k Hz audio
- ITU G.722.2 – Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband AMR-WB Vocoder Algorithm
- G723.1 – 5 1/3k and 6.4k bps ACELP/MP-MLQ
- ITU G.726 – 16k, 24k, 32k and 40k bps ADPCM
- ITU G.728 – 16k bps LD-CELP
- ITU G.729 – 8k bps CS-ACELP
- ITU G.729A – 8k bps CS-ACELP
- ITU G.729A Annex B – Silence Detection
- G.729.1 – Embedded Variable Bit-Rate
- GSM Speech Coders
- Other Speech Coders
Audio and Voice Processing
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
- Packet Loss Concealment (PLC)
- Adaptive Jitter Buffer
- Voice/Facsimile/Data Modem Detection
- Variable Playback / Pitch Corrected Rate Converter
- Audio Sample Rate Converter
Echo Cancellers
Video Codecs

Lawful Interception
Radio
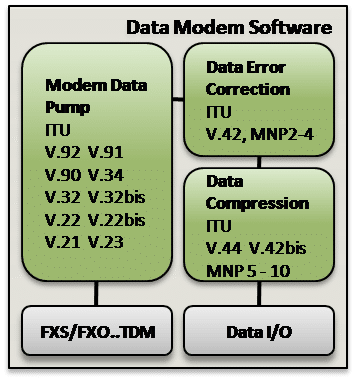
Modem
- V.92 Server/Client/Digital Client 28,000 – 56,000 bps downstream, 24,000 – 48,000 bps upstream,
(Block Diagram) - V.90 Server/Client/Digital Client 28,000 – 56,000 bps downstream, 4,800 – 33,600 bps upstream,
(Block Diagram) - 56k modem 28,000 – 56,000 bps downstream, 4,800 to 33,600 bps upstream,
(Block Diagram) - V.91 All Digital Mode, 28,000 to 64,000 bi-directional
- V.34 2400 to 33,600 bps
- V.32/V.32bis 4800 to 14,400 bps
- V.23 75 – 1,200 bps
- Bell 202 75 – 1,200 bps
- V.22bis 1,200 and 2400 bps
- V.22 1,200 bps
- Bell 212 1,200 bps
- V.21 300 bps
- Bell 103 300 bps
- V.42 LAPM Error Correction, Detection
- V.42bis Lempel-Ziv Data Compression
- V.44 LZJH Data Compression
- MNP 2-4 Error Correction
- MNP 5 Data Compression
- MNP 10 Protocol Extensions for Cellular
Modem over IP
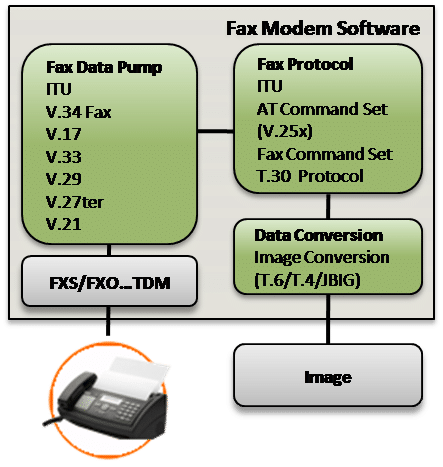
Group 3 Facsimile
- V.34fax – 2400 to 33,600 bps
- V.17 – 7200, 9600, 12,000 and 14,400 bps
- V.33 – 12000 and 14400 bps
- V.29 – 7200 and 9600 bps
- V.27ter – 2400 and 4800 bps
- V.21 Channel 2 – 300 bps FSK
- T.30 Fax Protocol
- T.30-E Color Fax Protocol
- T.30 Error Correction Mode
- Image Format Conversion
- T.6, MMR Image Format Conversion
- JBIG Image Format Conversion
- T.4 Copy Quality Checking/Correction
- Industry Standard Command Set
- V.250 (V.25ter) Command Set
- V.251 Command Set
- V.252 Command Set
- V.253/IS-101 Voice Command Set (Fclass 8)
- T.32 Fax Class 2.1 for V.34Fax
- T.31 Fax Class 1/1.0 (EIA-514)
- Fax Class 2/2.0 (EIA-592)
- Custom Command Set
Fax over IP
- T.38 Real-Time Fax Relay Over IP
- T.38 V.8/V.34 Extensions
- T.38 Spoofing Extensions
- T.37 Store and Forward Simple and Full Modes
- Block Diagram
Telephony
- North American Dialing Procedures
- North American Call Progress Generation/Detection
- International Dialing Procedures
- International Call Progress Generation/Detection
- DTMF Generation/Detection
- Caller ID Type I and II
- Call Waiting/Call Forwarding/Call Block features
- Acoustic, Line, and Digital Network Echo Cancellers
- General Purpose Tone Detectors/Generators
- Ring detect and distinctive ring detect
- Automatic Gain Control
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
- Packet Loss Concealment (PLC)
- Adaptive Jitter Buffer
- Voice/Facsimile/Data Modem Detection
- Multi-tasking environment compatible
Digital Telephony
- ISDN Interface
- V.110 Rate Adaptation
- V.120 Rate Adaptation
- HDLC B Channel (7 or 8 bit)
Telephony Signaling
- MF Generation/Detection
- MF R2 Compelled/Semi-Compelled Signaling
- MF R1 Signaling
- TIA 468A DTMF Signaling
- Bellcore Interoffice Signaling
- Q.921 LAPD Protocol
- Q.922 LAPF Protocol
- Q.931 ISDN Call Signaling
- Q.932 Frame Relay Call Signaling
3G Cellular
- 3G-AMR Vocoder
- Transceiver Implementation
- Turbo Decoder
Speakerphone
- Overview
- Half-Duplex Speakerphone for Low MIPS
- Full Duplex Speakerphone for High Performance
- Echo Cancellation
- Acoustic Echo Canceller (AEC)
- Audio over IP
Security and Cryptography
Nat/Firewall Support
- Overview
- BOOTP – Protocol (RFC 1497)
- DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (RFC 2131)
- MIB I (RFC 1156)
- RIP – Routing Information Protocol (RFC 1058)
- RIP 2 – Routing Information Protocol (RFC 1723)
- STUN – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs (RFC 3789)
- PPP – PPP – Point to Point Protocol (RFC 2153)
- PPPoE – PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
- Gateway and DMZ Port Forwarding
STUN, TURN and ICE
- Overview
- STUN – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs (RFC 8489, previously RFC 5389)
- TURN – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs (RFC 8656, previously RFC 5766)
- ICE – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs (RFC 8445, previously RFC 5245)
LANsEND Network Stack
- Overview
- IPv4 – Internet Protocol Version 4 (RFC 791)
- TCP – Transmission Control Protocol (RFC 793, RFC 1323)
- UDP – User Datagram Protocol (RFC 768)
- TCP/IP Header Compression (RFC 1144)
- PPP – Point to Point Protocol (RFC 2153, RFC 1662)
- PPPoE – PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
- PAP/CHAP Authentication (RFC 1994)
- IPCP – Internet Control Protocol (RFC 1332)
- ICMP – Internet Control Message Protocol (RFC 792)
- ARP – Address Resolution Protocol (RFC 1027)
- RARP – Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RFC 903)
- BGP – Border Gateway Protocol (RFC 1771)
- BOOTP – Protocol (RFC 1497)
- DHCP – Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (RFC 2131)
- FTP – File Transfer Protocol (RFC 959, RFC 2228)
- TFTP – – Trivial File Transfer Protocol (RFC 1350, RFC 2228)
- HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol (RFC 2616, RFC 2228)
- MIB I (RFC 1156)
- MIBII (RFC 1213)
- RIP – Routing Information Protocol (RFC 1058)
- RIP 2 – Routing Information Protocol (RFC 1723)
- SliP – Serial Link Internet Protocol (RFC 1055)
- SNMP – Simple Network Management Protocol (RFC 1155,
RFC 1157,
RFC 1215,
RFC 1351,
RFC 1352,
RFC 1353,
RFC 1420,
RFC 3411,
RFC 3412,
RFC 3414,
RFC 3415) - NTP – Network Time Protocol (RFC 1305)
- SNTP – Simple Network Time Protocol (RFC 2030)
- STUN – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs(RFC 3789)
- Telnet – Telnet Protocol (RFC 854)