G 711 Codecs and G 711a codecs
- Wideband audio codec
- 64 kbps PCM A-law and μ-law
- High quality speech for VoIP
- Real-time multi-channel implementation
- Optimized for DSPs, RISC, CISC processors
- ITU G.711 Appendix I and II compliant
G.711 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is a commonly used waveform for speech encoding and is suitable for use as an internet wideband audio codec in VoIP applications. Contact us to discuss your G.711 vocoder requirements.
VOCAL’s G 711 codec source code is optimized for leading DSPs and RISC/CISC processors from TI, ADI, ARM, Intel and other vendors. Custom designs are available to meet specific voice codec requirements. The G.711 codec may be licensed as a standalone voice compression algorithm, a library, or with a VoIP stack.
G.711 PCM
The G.711 PCM codec algorithm uses a sampling rate of 8,000 samples per second, with a tolerance on that rate of 50 parts per million (ppm). Non-uniform quantization with 8 bits is used to represent each sample, resulting in a 64 kbps bit rate.
There are two slightly different G.711 PCM versions; μ-law, which is used primarily in North America, and A-law, which is used by most other countries in the rest of the world. While μ-law tends to give more resolution to higher range signals, G.711 A-law provides more quantization levels at lower signal levels.
When using G.711 μ-law in networks where suppression of the all 0 character signal is required, the character signal corresponding to negative input values between decision value numbers 127 and 128 should be 00000010 and the value at the decoder output is -7519. The corresponding G.711 decoder output value number is 125.
G.711 Appendix I
ITU G.711 Appendix I outlines a Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) algorithm, also known as a frame erasure concealment algorithm. PLC can help hide transmission losses in a packetized network, specifically, in an audio system where the input signal is encoded and packetized at a transmitter first before being sent over a network where it is received at an end point, decoded and output as audio. Like G.711, many of the standard CELP-based speech coders, such as G.723.1, G.728 and G.729, also have PLC algorithms built into their standards.
G.711 Appendix II
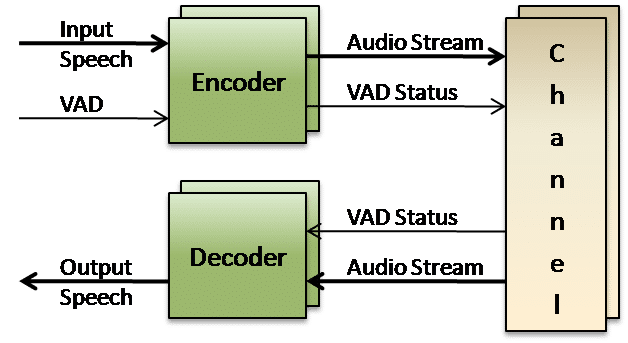
ITU G.711 Appendix II defines a standard method to perform Discontinuous Transmission (DTX) in a packet-based multimedia communication system. DTX utilizes the fact that a significant amount of voice traffic may not contain any speech but only background noise. This can be detected using Voice Activity Detection (VAD) and therefore fewer, smaller packets may be transmitted. Since audio is no longer transmitted in a continuous stream, Comfort Noise Generation (CNG) mimics the background silence.
Features
- Compliant with G.711 specification
- Compliant with G.711 Appendix I and II specifications
- Optimized for high performance on leading edge DSP architectures
- Multichannel implementation
- Multi-tasking environment compatible
- 64 kbit/s expander input rate
- 104 or 112 kbit/s expander output rate
- A-law or μ-law expander input
- Uniform PCM expander output
- 104 or 112 kbit/s compressor input rate
- 64 kbit/s compressor output rate
- Uniform PCM compressor input
- A-law or μ-law compressor output
- Selectable frame/buffer memory size according to the system needs
- MISRA compliant version (with limited deviations) available
Configurations
- DAA interface using linear codec at 8.0 kHz sample rate
- Direct interface to 8.0 kHz PCM data stream (A-law or μ-law)
- North American/International Telephony (including caller ID) support available
- Simultaneous DTMF detector operation available – (less than 150 hits on Bellcore test tape typical)
- MF tone detectors, general purpose programmable tone detectors/generators available
- Data/Facsimile/Voice Distinction available
- Common compressed speech frame stream interface to support systems with multiple speech coders
- Dynamic speech coder selection if multiple speech codecs available
- Can be integrated with Acoustic Echo Canceller, G.168 Line Echo Canceller and Tone Detection/Regeneration modules
- Available with VoIP stack
More Information
- G.711 PCM Audio Examples
- PSQM/PSQM+ values for G.711
- G.711 PCM MIPS/memory requirements
- ITU Recommendation G.711 and Appendices
Platforms
VOCAL’s optimized vocoder software is available for the following platforms. Please contact us for specific G.711 codec supported platforms.
| Processors | Operating Systems |
| · Texas Instruments – C6000 (TMS320C62x, TMS320C64x, TMS320C645x, TMS320C66x, TMS320C67x), DaVinci, OMAP, C5000 (TMS320C55x) · Analog Devices – Blackfin, TigerSHARC, SHARC · PowerPC · MIPS – MIPS32, MIPS64, MIPS4Kc · ARM – ARM7, ARM9, ARM9E, ARM10E, ARM11, StrongARM, ARMCortex-A8/A9/A15/A3x/A5x/A7x, Cortex-M3/M4/M7/M33 · Intel / AMD – x86, x64 (both 32 and 64 bit modes) | · Google Android · Apple iOS / iPhone / iPad & MacOS · Unix, Linux, μClinux, BSD · Microsoft Windows ACM / RTC / CE / Mobile · Symbian · eCOS / eCOSPro · Wind River VxWorks · Green Hills Integrity · VOCAL LANsEND · Micrium μCOS |