VoIP Decoding extracts audio and video from intercepted VoIP communications sent over mobile, LTE, and other IP networks. VOCAL’s VoIP decoder software may be used for lawful interception and business to decode multimedia transmissions from previously recorded files and real-time data streams. Decoded communications are output to standard file types. Audio and video decoding is available for a wide range of voice and video compression algorithms.
VOCAL has substantial experience with VoIP lawful interception and recording technologies and can advise in the proper configuration of VoIP traffic analysis and recording systems. Our expertise with VoIP communications protocols is essential for extracting data of interest from the large volumes of network traffic that can be collected. For partial or damaged recordings, manual analysis may be able to recover some or all of the relevant data.
Software Features
- Automatic classification of voice, video, data, facsimile and non-standard or custom types
- Extract and decompress the data of interest to standard file types
- Information about extracted data is provided to the user
- Support real-time processing on a continuous stream and pre-recorded data
- Support secure protocols including SRTP and SSL / TLS
- Support manual processing of partial or damaged recordings
- Automatic and forced detection of non-standard signaling
- Extract data in auto, manual and polling modes
- Extract Caller ID, DTMF/MF tones and pulse dial information
- Support libpcap network traffic captures
- Support Windows and Linux operating systems, as well as embedded system platforms
- Available as an executable or library (.dll/.so)
- Available with our turn-key ATA hardware reference design
VoIP Decoder Software
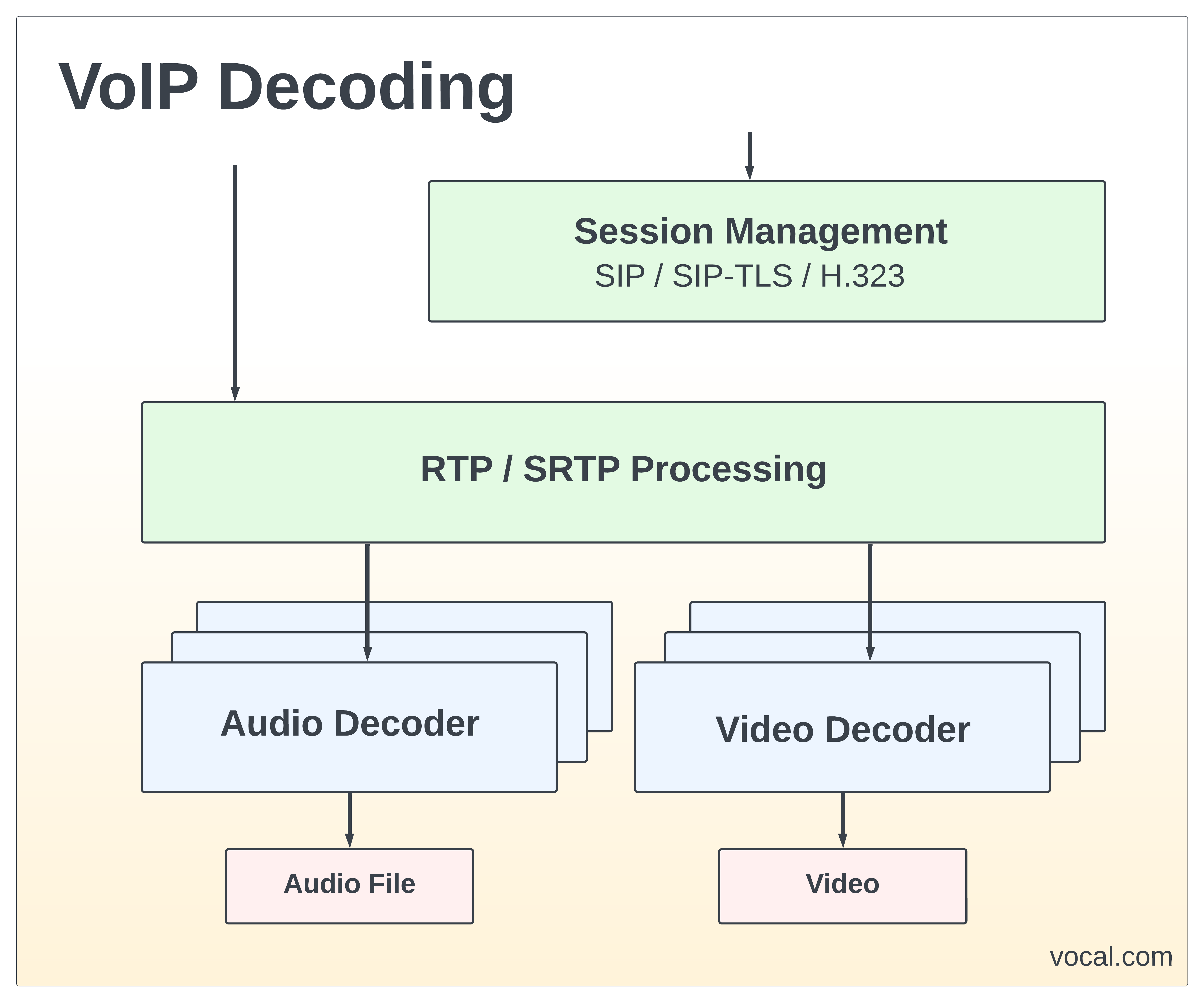
VoIP Decoder software enables a lawful interception application to decode audio and video from intercepted multimedia communications as recorded files or real-time data streams. The library supports decoding of VoIP protocols including SIP, SDP, RTP/SRTP, RTCP and RTSP as well as SSL and TLS.
A VoIP session is established using SIP and SDP packets which identify the endpoints and the method, media and other session parameters for communications.
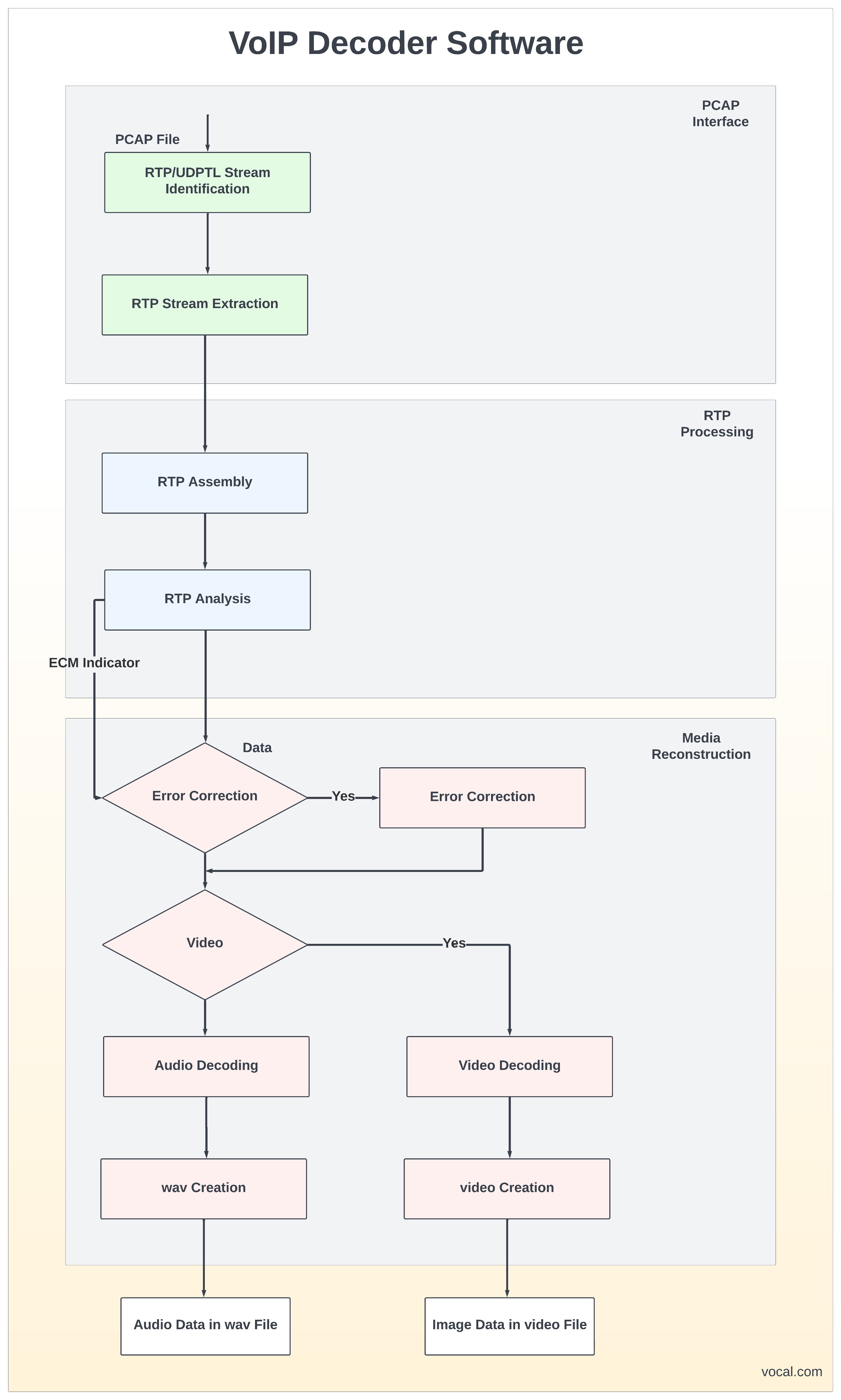
During a VoIP multimedia session, audio and/or video is transmitted over an IP network as RTP packets. Data can be transferred using TCP, UDPTL over UDP, or RTP over UDP. By using the sequence numbers in each packet, along with any redundant or forward error correction (FEC) packets sent, the full media stream can be reconstructed and processed by the appropriate codec to reproduce the original content.
VoIP Decoding software extracts audio and video communications from VoIP recorded files or live network traffic.
Input Data Format
The VoIP Decoding Library accepts both file-based and packet-based input for audio and video decoding. The file input into the library is a libpcap capture file, e.g. the output produced from a Wireshark trace. The capture file must contain the session control messages (SIP and SDP) sent by both participants during the session, and can contain any amount of RTP and non-RTP traffic. These messages will be used to reproduce the audio and video transferred during the call session. It is preferred that as much of the session transmission as possible is provided in the capture file, as the absence of certain messages may result in failure to extract the audio and video. When possible, partial output will be provided.
In addition, the data packets can be input directly into the library, enabling real-time processing of RTP streams. When using this approach, the user of the library is responsible for initializing and shutting down the VoIP processing.
Output Data Format
The output file format of the VoIP decoder will be an audio .wav file and/or an appropriate video file format but other formats may be chosen for a specific implementation. Typically one output file is created per input, named in increasing numerical order and extracted from the recordings. A detailed logfile of each VoIP session is also available from the software to assist in debug and analysis.
To summarize the audio and video output, a short report file is produced that contains the following information: input file, source IP/port, destination IP/port, and for each file: length and compression.
Audio Codecs
- ITU Speech Coders
- G.711 – 64k bps PCM (A-law or μ-law form)
- G.722 – 7 kHz audio coding within 64 kbit/s (SB-ADPCM)
- G.722.1 – 24k and 32k bps, 7 kHz audio
- G.722.2 – Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (GSM AMR-WB)
- G.723.1 – 5 1/3k and 6.4k bps ACELP/MP-MLQ
- G.726 – 16k, 24k, 32k and 40k bps ADPCM
- G.727 – 5, 4, 3 and 2-bits sample Embedded ADPCM
- G.728 – 16k bps LD-CELP
- G.729/G.729A – 8k bps CS-ACELP
- G.729 Annex B – Silence Detection
- GSM Speech Coders
- GSM-FR – GSM 06.10 Full Rate Vocoder
- GSM-HR – GSM 06.20 Half Rate Vocoder
- GSM-EFR – GSM 06.60 Enhanced Full Rate Vocoder
- GSM-AMR – GSM 06.90 Adaptive Multi-Rate Vocoder
- GSM-AMR-WB – 3GPP TS 26.171 Adaptive Multi-Rate Wideband (ITU G.722.2)
- Wideband Speech Coders
- Other Speech Coders
Video Codecs
VOCAL’s VoIP Decoder software library source code is optimized for DSPs, ARM and microprocessors from TI, ADI, Intel, and other leading vendors. Custom VoIP decoding solutions are also available. Contact Us to discuss your VoIP interception and decoding requirements.

VOCAL’s solution is available for the above platforms. Please contact us for specific supported platforms.