Session Border Controller (SBC)
 VOCAL’s Session Border Controller (SBC) is designed to streamline call routing and enhance interoperability. The SBC routes calls between peers based on phone numbers or specific conditions, ensuring smooth operation with various manipulations. It also boasts a robust configuration database for seamless management, codec negotiation, custom headers forwarding, and handling of essential call messages. With advanced routing capabilities, message manipulation, and call admission control, the SBC also supports multi-network SIP interfaces, secure TLS signaling, and high availability with call continuity. Contact us today about our SBC.
VOCAL’s Session Border Controller (SBC) is designed to streamline call routing and enhance interoperability. The SBC routes calls between peers based on phone numbers or specific conditions, ensuring smooth operation with various manipulations. It also boasts a robust configuration database for seamless management, codec negotiation, custom headers forwarding, and handling of essential call messages. With advanced routing capabilities, message manipulation, and call admission control, the SBC also supports multi-network SIP interfaces, secure TLS signaling, and high availability with call continuity. Contact us today about our SBC.
VOCAL Session Border Controller (SBC)
VOCAL’s SBC offering facilitates effortless VoIP call management and seamless interoperability. Built on VOCAL’s proven operational reliability. With robust management and monitoring the SBC excels and scales according to your needs. Hierarchical access for configuration, monitoring and auditing with version history for all changes allows rapid testing and deployment as well as reliability.
SBC provides all the fundamental call establishment functionalities, as well as rule-based session negotiation capabilities depending on customer needs. All typical VoIP interoperability functionalities, such as early media handling and message manipulation capabilities are included, with in-depth customization possibilities.
Overview
Our SBC delivers advanced call management through intelligent routing and stateful manipulation. In addition, the SBC excels in routing flexibility, supporting exact-match phone number algorithms, condition-based rules using SIP headers, and blind routing without preconditions.
Comprehensive message manipulation enhances customization, leveraging pre- and post-parsing with regexes and headers. Call admission controls regulate inbound and outbound rates, enabling shared call limits for provider pools and enhancing performance. Call classification further optimizes call flow management.
With support for multiple network/SIP interfaces, the SBC offers seamless operation across environments, even behind NAT configurations. Our SBC supports secure signaling with TLS.
High availability with call continuity ensures reliability during failover scenarios, preserving active sessions. Detailed Call Detail Records (CDR) and accessible debugging logs enhance monitoring and maintenance, while a solid reporting framework provides actionable insights.
Simple Configuration
Designed to meet modern telecommunication demands, the SBC balances robust functionality with reliability, making it a cornerstone for efficient and secure communication systems.
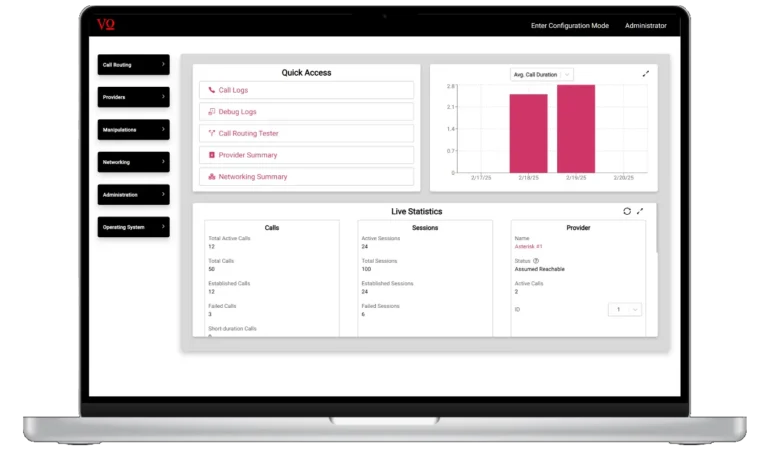
VOCAL’s Session Border Controller also features a user-friendly web interface for configuring the SBC database, viewing live statistics, exporting logs, testing call routing configurations, and more.
These features collectively make the SBC an indispensable tool for managing complex communication networks, ensuring reliable, secure, and efficient call routing and handling.
Session Border Controller Features
- Configuration database:
- Accessible via user-friendly web interface
- Upgradeable DB schema
- Revisioned configurations with rollback capabilities
- Basic call establishment:
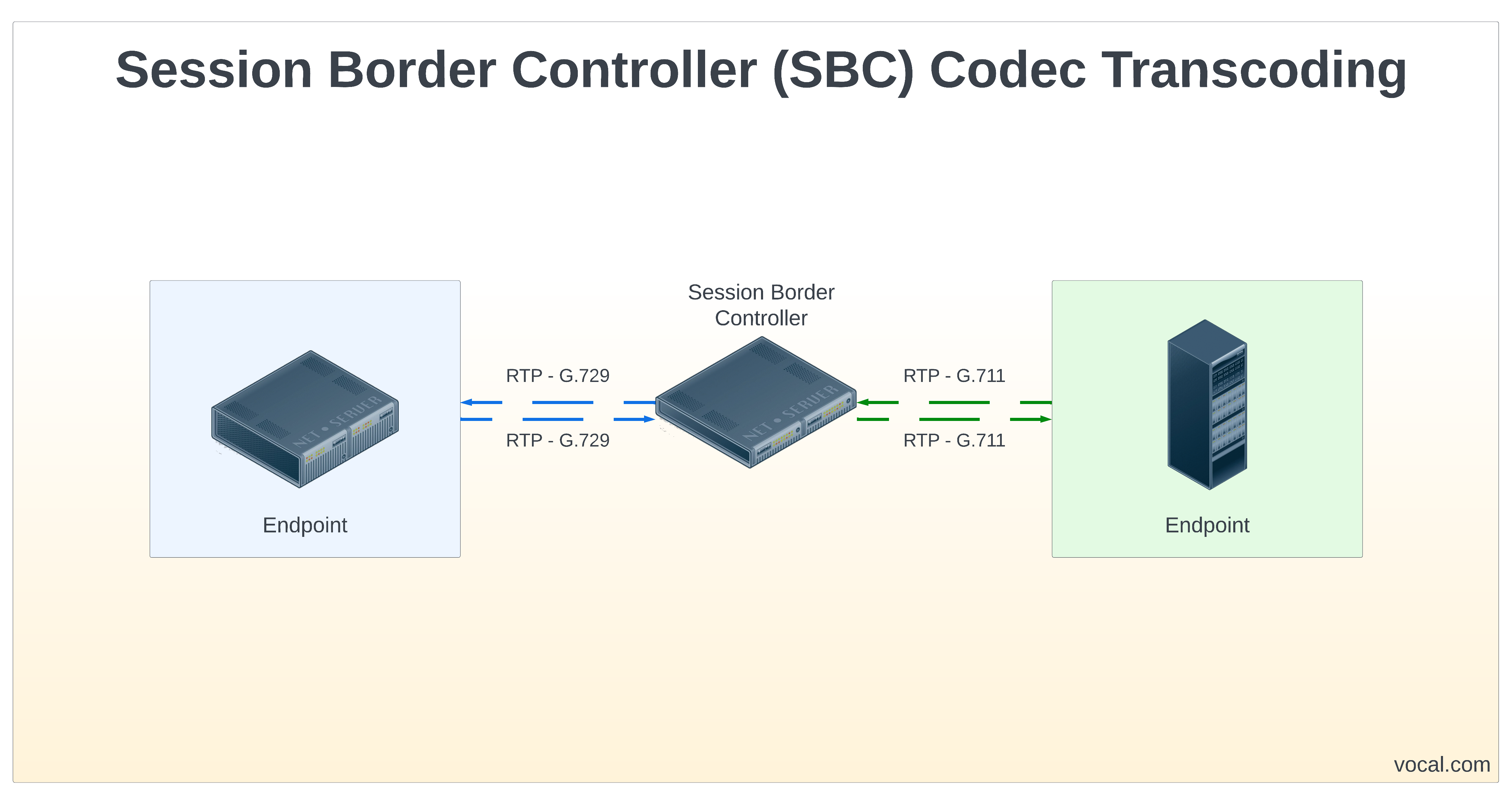
- Codec negotiation
- Rejection of calls with disallowed codecs
- Early media (183 session in progress)
- Delayed offer
- Custom headers forwarding
- RE-INVITE handling/passthrough
- Placing calls on hold
- Changing media destination during a call
- Handling of PRACK messages with interoperability options
- Handling of UPDATE messages with interoperability options
- Stateful manipulation:
- Querying external server
- Informational response type manipulation (183 ↔ 180)
- Conversion of delayed to early offer
- RE-INVITE handling (transparent/locally terminated)
- Hold method manipulation (sendonly vs. inactive)
- Routing:
- Blind routing without conditions
- Most-exact-match lookup algorithm
- Supports ranges, prefixes, wildcards
- Routing based on condition, prefix/suffix/contains/exact/present match, custom headers
- Backup routes if provider is unresponsive (OPTIONS ping not responding, or fails to respond to INVITE)
- Weighted load balancing
- Handling of redirections (3xx)
- Support for Route Headers
- REGISTER request routing and proxying
- Message manipulation:
- Pre-parsing manipulation using regexes
- Post-parsing manipulation with headers
- Allows saving data to variables and recalling
- Allows cascading manipulation rulesets
- Conditions and branching
- Logging and optionally filtering unknown headers
- Call admission control (CAC):
- Shareable pools with call and rate limits by inbound/outbound/total per pool
- Support for multiple network/SIP interfaces:
- Define multiple interfaces/sockets and bind providers
- Handles scenarios where interface is behind 1:1 NAT with knowledge of the “public” IP address
- Media latching:
- Support for cases where media does not come from the address specified in SDP
- TCP SIP scaling:
- Utilizing the same TCP session for all SIP messages
- Call forwarding/diversion:
- Handling of REFER messages
- TLS support for signaling:
- High availability with call continuity
- Reporting (CDR) and easy debugging log output
- Transcoding bypass
- Exportable statistics
- Call Routing Tester
- Live statistics
Custom Session Border Controller Solutions
The fully software-based architecture utilized by our SBC combined with decades of experience with telecommunications means that VOCAL can customize interfaces and functionality specific to you. Please contact us for information about custom solutions.