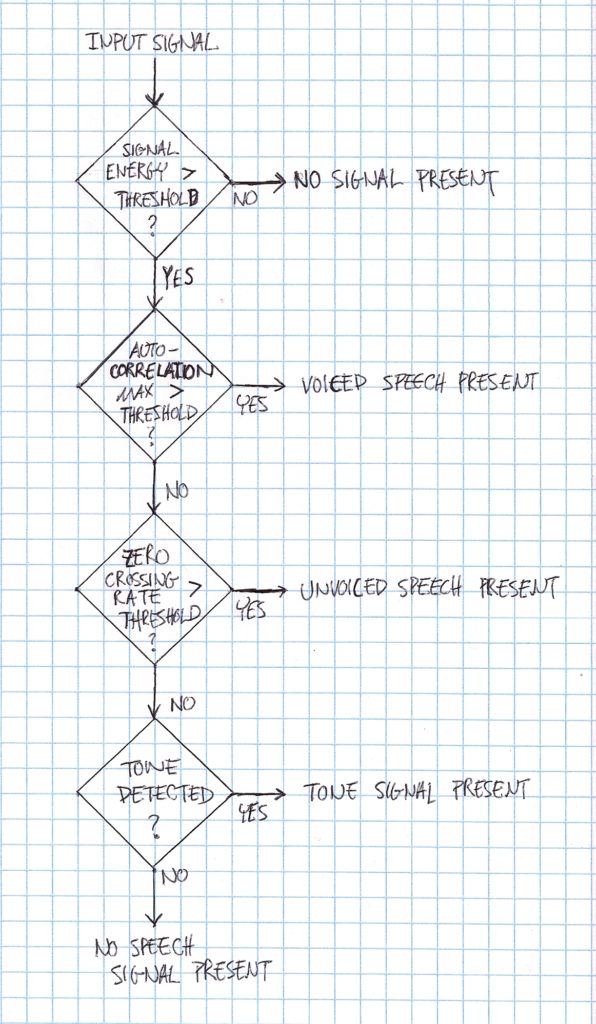
In voice communications and speech applications, voice activity detectors(VAD), tone detectors and voiced/unvoiced classification play a crucial role to the success of a product. For example, in military radios with voice activated transmssion (VOX) the VAD must detect speech activity 99% of the time, but should not trigger on tones and impulsive noise sources. False positives on noise and false negatives of speech would make a radio unusable in the field. In order to have a robust decision four main components are required: a signal energy detector, autocorrelation pitch detector, tone detector, and the zero crossing rate.
The first component is a signal energy detector. This simply just calculates the current signal energy of and compares this value to the long term signal energy average. If the signal energy is greater than the long term average by a certain threshold then there is a signal of interest. What type of signal it is is unknown, more detectors are needed.
To help distinguish the type signal that is present, the autocorrelation of the signal is performed. If there is a strong correlation at a delay that would correspond to a fundamental frequency of speech ranging from 100 Hz to 600 Hz, then the VAD can be confident that it has found a that voiced speech frame has been found.
If the frame was not a voiced speech frame, then the zero crossing rate can be used to determined if the signal energy is unvoiced speech. Voiced speech due to its low periodic signal characteristics will have a low zero crossing rate, while unvoiced speech signal energy is dominated in the upper frequencies and have a high zero crossing rate.
If the frame was not voiced or unvoiced speech, then a tone detector can be used to determine if there is a dominant sinusoidal signal present above 600 Hz. However, at this point it is unlikely the signal is speech related, it is important to classify the signal. There are many different approaches to determine the presence of a tone, such as the Goertzel algorithm or the Teager-Keiser energy operator.
After the running the all of these detectors and classifiers, the VAD will able to reliably and confidently determine whether a speech signal is present. Figure 1 shows a simplified block diagram of the VAD decisions.
VOCAL Technologies, Ltd. offer a VAD solution that has been successfully deployed in the most adverse acoustic scenarios. Please contact us to learn more about our solutions.