Received signal energy based voice activity detectors, VADs, are widely employed in broadband acoustic systems. There is a potential drawback in scenarios where there is high energy ambient noise. Cross correlation based VADs also have some drawback due to some level of correlation between noise samples of microphones due to their proximity to each other. An alternative approach is to use a combination of eigenvalues and coherence. The case of two microphones is discussed below.
Consider a far field acoustic signal impinging microphones with separation distance
at an angle of
. The signal at microphone
,
, can be denoted as
where is the delay of the desired signal at microphone
if present,
is the delay of the noise signal at microphone
with the expectation
,
is the source signal,
is noise and
is the speed of acoustic signals.
Both and
are zero mean ergodic processes. The decision problem is whether a frame contains a signal or is a noise frame.
We utilize the imaginary value of the coherence, , given by
and note that for a pure noise signal , . Further the eigenvalues of the frame co variance matrix will have the largest eigenvalue orders of magnitude larger that the smallest eigenvalue. The largest eigenvalue will correspond to the speech signal if present. Denote the eigenvalues as
and
. We form a metric
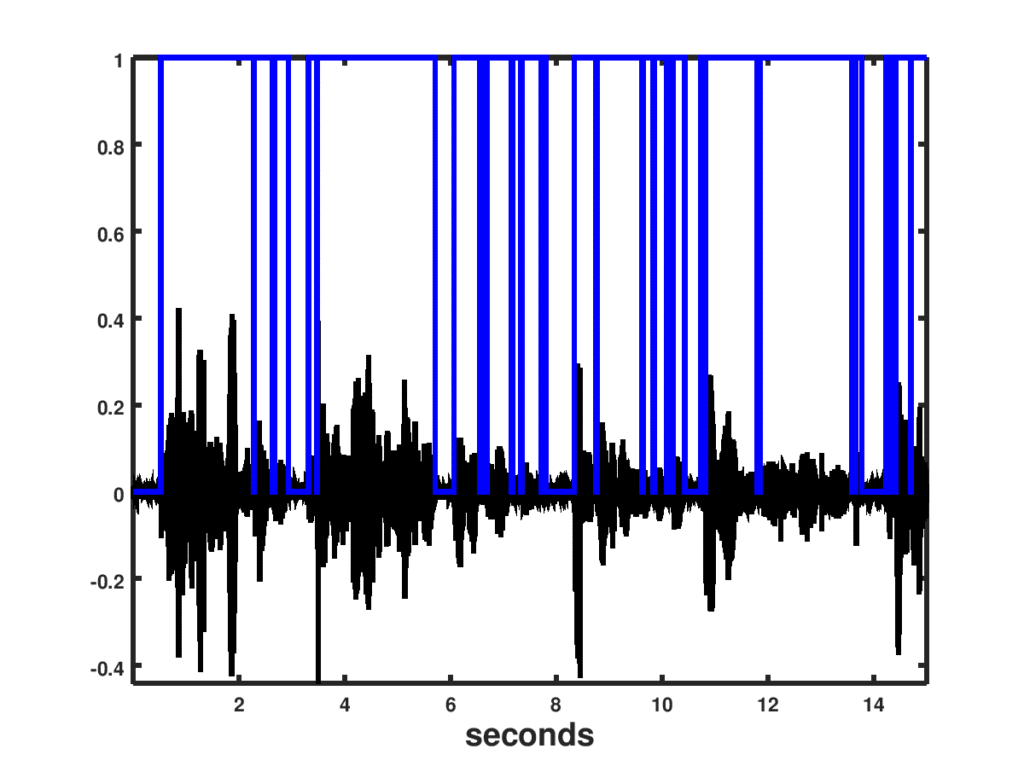
and compare the metric to the noise floor which is a function of previous values of noise only frames. A sample of the performance of this VAD is shown on the Figure below.
Result from VAD
VOCAL Technologies offers custom designed direction of arrival estimation solutions for beamforming with a robust voice activity detector, acoustic echo cancellation and noise suppression. Our custom implementations of such systems are meant to deliver optimum performance for your specific beamforming task. Contact us today to discuss your solution!