Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (MPEG-DASH) is an adaptive-bitrate streaming technique that allows high quality audio/video content streaming over the Internet using conventional HTTP web servers.
HTTP web server infrastructure is used for delivery of essentially all World Wide Web content. MPEG-DASH is the first adaptive-bitrate HTTP-based streaming solution that is an international standard. The technology was developed under MPEG.
There are proprietary HTTP streaming technologies such as Apple HTTP Live Streaming (Apple HLS), Adobe HTTP Dynamic Streaming (Adobe HDS), and Microsoft Smooth Streaming. They use different manifest and segment formats. To receive content from each proprietary server, a device must support the proper protocols.
The MPEG-DASH standard provides a full set of features for HTTP adaptive-bitrate streaming that allow a standard-based client to be able to receive content from any standard-based server, thereby enabling interoperability between servers and clients of different vendors.
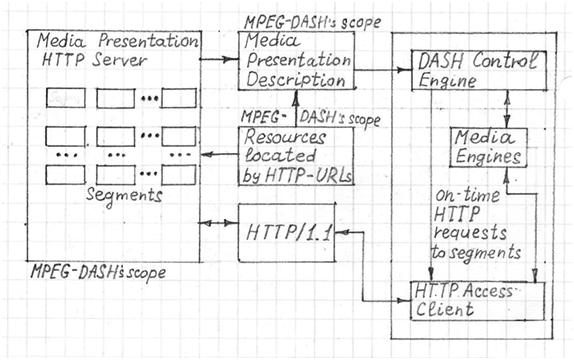
An MPEG-DASH server provides client players with a list of the available media segment URLs in a Media Presentation Description (MPD) file. Clients can then sequentially request the media segments as required to provide uninterrupted playback of the media presentation.
To play the content, the client obtains the MPD from the MPEG-DASH server. The MPD can be delivered using HTTP, email, thumb drive, broadcast, or other transports. The MPD contains information about the content characteristics such as content availability, media types, timing, resolutions, minimum and maximum bandwidths, location on the network (media segment URLs), accessibility features and required digital rights management (DRM).
Based on the MDP information, the client selects an appropriately encoded stream and sends the request to start streaming.
Received media segments are buffered by the client to handle network variations. During playback, the client monitors fluctuations in the network bandwidth. Based on this information, the client may switch to receive segments with lower or higher bitrate.
The same content may be available at different servers or content delivery networks (CDN). The client can stream from any of them to maximize the available network bandwidth. In this case, the MDP provides multiple URLs for the same segment.
The MPEG-DASH standard is codec and container agnostic (H.264/AAC, WebM, etc. and different media containers). It also supports: closed-captions and subtitles, multiple file container formats, video-on-demand (VoD) and live streaming.
The duration of segments can vary for both VoD and live streaming. For live streaming, the duration of the next segment can also be signaled within the current segment.
MPEG-DASH VoD or live content can be encrypted using various DRM schemes. The decryption key information is delivered to the client by MPD.
The MPD can be divided into multiple parts and downloaded in multiple steps. Some of its elements can be externally referenced.
MPEG-DASH combines delivery formats into DASH profiles. These profiles specify features for interoperability. They are identified in the MPD by unique uniform resource names (URNs).
Each segment can contain information about UTC time, so clients can control their clock drift.
A set of quality metrics are defined in the standard. Measurement happens at the client side and the information is sent back to the server.