Whether you are aware of it or not, speech coders play a role in our daily lives. They are used in smart phones, VoIP phones, conferencing systems, military radios, mining radios, intercom systems, etc. Over the past 30 years, a large number of voice coders (vocoders) have been developed and standardized by the telecommunications industry. This article will explain how to choose the best speech coder for your next product design.
When choosing a speech coder the following questions must be asked:
What is the required/desired audio sampling rate of the system?
What is the maximum allowable data rate of the system?
What is the maximum allowable CPU or power consumption allowed by the speech coder?
What is the acceptable speech quality of the system?
With speech coders there are general trends for the engineering trade-offs between these various system constraints. For example, as the data rate decreases, the computational complexity tends to increase. As the data rate decreases, the speech quality the vocoder decreases.
The tables below show where the most popular speech coders used by VOCAL’s customers fall within each of these constraints.
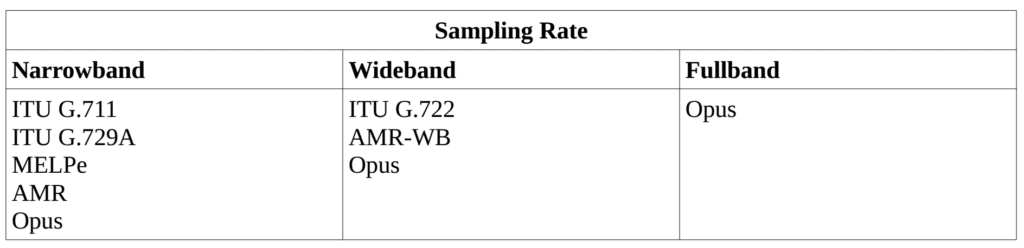
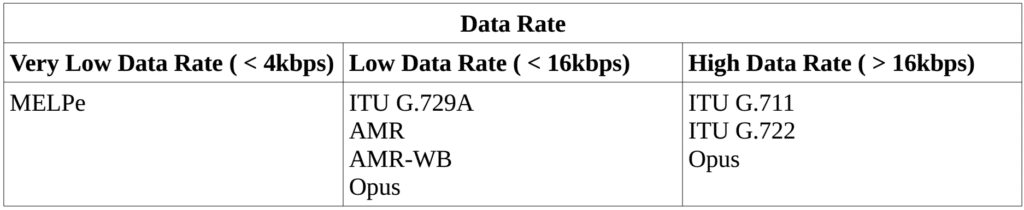

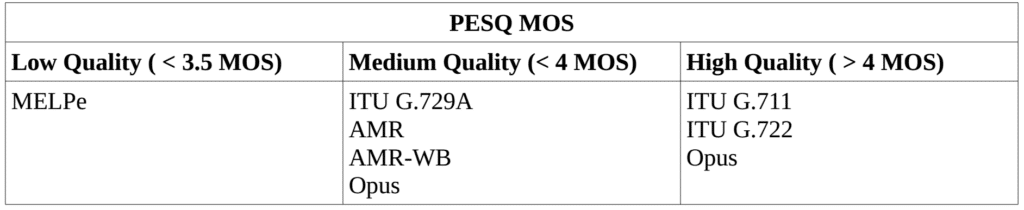
Opus appears in so many different categories by design. Opus can be use at various different sampling rates, the bit rate is configurable and the complexity is configurable. However, the trade-off for this complexity is that the memory requirement is large. If the application/product has a more focused design, then Opus is not recommended. At 8kHz sampling, the ITU G.729A provides the best trade-off between computational complexity, bit rate and speech quality, and for very low bit rates MELPe is the best choice.
VOCAL Technologies, Ltd. has a large offering of ITU, GSM, wideband and industry standard voice codecs optimized for execution on ANSI C and leading DSP architectures (TI, ADI, AMD, ARM, MIPS, CEVA, LSI Logic ZSP, etc.). Please contact us to learn more.