MVoIP and Mobile VoIP Software
Mobile VoIP software libraries provide native MVoIP solutions for iPhone & iPad and Android phones, tablets and other mobile devices. These libraries extend the developer’s toolset with our native software development kit (SDK) that includes VoIP stacks, industry standard voice codecs and our robust Speech Enhancement algorithms.
- Android and iOS VoIP SDKs
- Native library with API
- Narrowband and wideband voice codecs available
- Echo and noise solutions for superior speech
- Full featured VoIP telephony
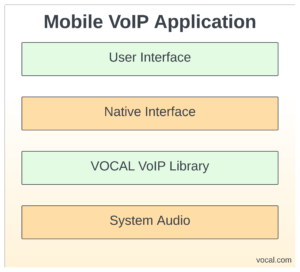
Our extensive experience in the design, implementation, and configuration of vocal mobile, network, and telephony applications will help you select the right solution for your mobile VoIP and VoWiFi applications. VOCAL’s MVoIP source code is optimized for DSPs and ARM processors from TI, ADI and other leading vendors. Contact us for a demo or to discuss your mobile VoIP requirements.
Mobile VoIP Software | MVoIP Software
VOCAL Mobile VoIP software is optimized for performance on DSPs and ARM processors for iOS/iPhone/iPad, Android and other mobile over IP devices and includes the following:
- Native library interface
- Mobile SIP stack with adaptive jitter control
- VoIP codecs support narrowband and wideband audio
- Speech enhancement with echo cancellation, noise reduction and dereverberation
- Beamforming for microphone noise reduction
- VoIP Software Modules
Android VoIP SDK
VOCAL’s Android VoIP SDK software library is optimized to meet unique SIP calling requirements for mobile over IP app developers with support for Android voice codecs, acoustic echo cancellation, and noise reduction algorithms. These libraries are developed in C/C++ for use with the Android SDK.
iOS VoIP SDK
VOCAL’s iOS VoIP SDK software library is optimized for custom mobile SIP client application development for iOS devices and include voice codecs as well as acoustic echo and noise cancellation algorithms. These libraries are developed in C/C++ for use with the iOS SDK.
Native SIP Stack
VOCAL’s SDK implements a native SIP stack with VoIP protocols, including SIP, SDP and RTP optimized for iOS, Android and other platforms. The native SIP stack provides access to the speech coders and other software modules and incorporates an adaptive jitter algorithm to further enhance voice quality. The robust jitter algorithm is exceptional at maintaining constant voice output to the listener while quickly and effectively adapting to packet loss and network delays.
Mobile VoIP Codecs
VOCAL Mobile VoIP libraries incorporate a selection of voice and audio codecs to customize applications for unique MVoIP requirements including a full range of ITU, GSM, Wideband, Android, iOS, and other industry standard voice codecs optimized for mobile platforms. Developers should evaluate the characteristics of each vocoder and its suitability for a particular application and/or platform. VOCAL has extensive experience with the selection and configuration of these voice codecs for optimal performance on ARM platforms.
Mobile VoIP Speech Enhancement
VOCAL Mobile VoIP libraries include speech enhancement for improved speech intelligibility with optimized echo cancellation, dereverberation, and noise reduction algorithms. Echo cancellation reduces reflected copies of a direct path wave from the acoustic / mechanical coupling between speaker and microphone; dereverberation handles reflections from surfaces in an enclosed environment; while noise reduction addresses additive noise sources, e.g. wind noise. The combination of these techniques produces superior speech in MVoIP applications.
Our mobile VoIP libraries also include acoustic beamforming algorithms to actively focus on and capture the speaker’s voice. Mobile devices are increasingly used as hands-free, speakerphone-like systems where the speaker is often located in a room (or automobile) some distance from the microphone. Beamforming takes advantage of newer mobile devices with multiple microphones to selectively capture the speaker’s voice while rejecting interferes and other sources of background noise.
Mobile VoIP Telephony Features
VoIP Protocols SIPv2 SDP RTP RTCP Network Protocols IPv4 TCP UDP ICMP RARP ARP DNS DHCP Client NTP SNTP STUN HTTP FTP/TFTP QoS NAT/Firewall Support Built-in Router NAT Traversal NAT Firewall Port Forwarding LAN Pass Through PPPoE Security Protocols SRTP SDES SSLv3/TLSv1 HTTPS IPsec | Encryption AES DES 3-DES CCMP RC4 SHA-1 RSA Voice Codecs G.711 G.723.1 – 6.4, 5.3 kbps G.726 – 16, 24, 32, 40 kbps G.728 G.729A G.729B iLBC Voice Features Voice Activity Detection (VAD) Silence Suppression (DTX) Comfort Noise Generation (CNG) Packet Loss Concealment (PLC) Dynamic Jitter Buffer (Adaptive) Audio Codec Preferences Dynamic Payload Negotiation Codec Name Assignment Configurable Frames per Packet G.168 Line Echo Cancellation 128ms Tail Length NLP Suppression Double-Talk Detection Fax Support G.711 Fax Pass-Through T.38 – Real-Time Fax Over IP T.38 using UDP T.38 using RTP | Telephony CLASS Features Call Waiting Enable/Disable Caller ID Display Enable/Disable Call Waiting Caller ID Enable/Disable Blocked Call List for a Specified # Distinctive Ring for a Specified # Block/Unblock Caller ID Block/Unblock Caller ID for One Call Accept Priority Call of a Specified # Busy Number Redial Call Return (Call the Last Caller) Deactivate/Activate Call Waiting Call Forwarding Speed Dial (8 + 20 Numbers) Block Anonymous Calls Do Not Disturb Call Transfer 3-way Conference Calling Redial Call Hold Call Waiting/Flash Flash Hook Timer Delay Disconnect Hot Line and Warm Line Calling Call Blocking with Toll Restriction Caller ID Generation Call Waiting Caller ID with Name/# Distinctive Ringing Distinctive Call Waiting TTY / TDD Support MWI – Tone and Visual VMWI Via FSK Polarity Control | Call Progress Tones Programmable Tone Generation Patterns Four Tones, Four On/Off Time Pairs
Ringing Patterns Programmable Ring Patterns Four On/Off Time Pairs
Distinctive Call Waiting Programmable Tone Generation Four Tones, Four On/Off Time Pairs 8 Distinctive Call Waiting Patterns |
SIPv2 – Session Initiation Protocol (RFC 3261, 3262, 3263, 3264)
SDP – Session Description Protocol (RFC 4566)
RTP – Real-Time Protocol (RFC 3550, 3551)
RTCP – Real-Time Control Protocol (RFC 3550)
RFC 4733 X-NSE Tone Events for SIP/RTP
RFC 4733 AVT Tone Events for SIP/RTP
STUN – Simple Traversal of UDP over NATs (RFC 3789)
SIPS – SIP Secure using TLS (RFC 3261)
SRTP – Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (RFC 3711, 4568)
MKI – Master Key Identifier (part of RFC 3711)
AES – Advanced Encryption Standard – supports 128/195/256 bit keys
HMAC – Authentication
IPv4 – Internet Protocol Version 4 (RFC 791)
TCP – Transmission Control Protocol (RFC 793)
UDP – User Datagram Protocol (RFC 768)
ICMP – Internet Control Message Protocol (RFC 792)
RARP – Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RFC 903)
ARP – Address Resolution Protocol (RFC 826)
DNS- Domain Name Server
DHCP Client – Dynamic Host Control Protocol (RFC 2131)
NTP – Network Time Protocol (RFC 1305)
SNTP – Simple Network Time Protocol (RFC 2030)
HTTP – HyperText Transfer Protocol
TFTP – Trivial File Transfer Protocol (RFC 1350)
PPPoE – Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
G.711 – Pulse Code Modulation
G.722 – Wideband ADPCM
G.722.1 – 24k and 32k bps 7kHz Wideband
G.722.2 – GSM-AMR-WB
G.723.1 – 6.4 and 5.3 kbps ACELP/MP-MLQ
G.726 – 16, 24, 32 and 40 kbps ADPCM
G.728 – 16 kbps LD-CELP
G.729 – 8 kbps CS-ACELP
G.729A – 8 kbps CS-ACELP Low Complexity
G.729B – Silence Detection/Comfort Noise Generation
G.729D – 6.4 kbps CS-ACELP
G.729E – 11.8 kbps CS-ACELP
GSM-FR – GSM 06.10 Full Rate Vocoder
GSM-AMR NB – GSM 06.90 Adaptive Multi-Rate
GSM-AMR WB – Wideband Adaptive Multi-Rate
iLBC – Internet Low Bitrate Codec
OPUS – 16KHz SILK, 22/24KHz CELT
Speex – 8 kbps CELP
MELPe – 2400/1200/600 bps Codec
TSVCIS – Tactical Secure Voice (Wideband MELPe)
LPC10 and CVSD – Legacy Voice Codecs
Q.24 DTMF Generation with Zero Crossing Cutoff
Q.24 DTMF Detection exceeding Bellcore Specifications
Configurable Tone Generation for 4 Sets of Frequencies and 4 Sets of On/Off Cadence
Programmable Precise Tone Detectors
G.168 Line Echo Cancellation
16/32/64 ms Echo Length
Nonlinear Echo Suppression (ERL greater than 28 dB for f = 300 to 3400 Hz)
Double-Talk Detection
Full Duplex Speakerphone
Narrow and Wideband Operation (8Khz and 16KHz)
Adjustable Tail Length (128 ms typical, 256 ms max)
Nonlinear Echo Processing with Comfort Noise Generation
Full Duplex Operation with Noise Reduction
Double-Talk detection, Low Divergence during Double Talk
Dual/Multi-Microphone Adaptive Noise Cancellation
Single Channel Noise Reduction
Active Noise Cancellation to identify and remove repetitive noise signals
Frequency Domain Noise Reduction
18dB Noise Reduction (typical)
Approximate 20msec Delay
Audio Beamforming (four or more mics)
Audio Null Forming
Direction of Arrival Estimation
Audio Beam Steering
Automatic Gain Control
Voice Compressor
Multiband Equalizer
Automatic Delay Estimation
Battle Field VOX
Voice Activity Detection
Noise Gating
Wind Noise Reduction
Click Noise Removal
VAD/DTX/CNG as per SCIP 210 Appendix B

VOCAL’s solution is available for the above platforms. Please contact us for specific supported platforms.