VOCAL’s Robust Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) software is an efficient, portable, customizable full-duplex audio solution for removing echoes caused by acoustic coupling and reverberations between the microphone and loudspeaker in the voice. Beyond adaptive filtering, double-talk detection, residual echo suppression, VOCAL’s AEC SDK can include features, such as noise reduction, anti-howling, automatic gain control and automatic delay estimation.
VOCAL’s AEC with speech enhancement features provide high definition and high-fidelity audio quality for full-duplex audio communications. VOCAL’s Robust Acoustic Echo Canceller software is platform independent C code, and is available for a wide variety of platforms, including ARM, Intel, ADI DSP, TI DSP. This software can be applied to audio applications with sampling rates ranging from narrowband (8kHz), wideband (16kHz), and fullband (48/96kHz).
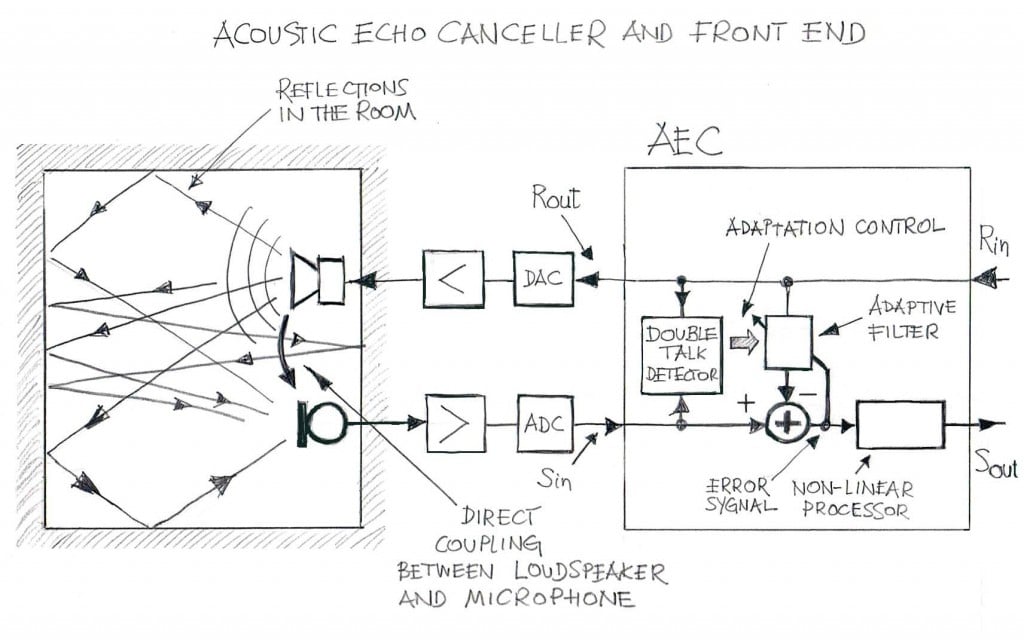
Acoustic echo cancellation removes echoes caused by acoustic coupling and environmental acoustic effects.
Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) software can be applied to hands-free telephone systems, conferencing speakerphones, IP intercom systems, V2oIP videoconferencing systems, aeronautical headsets, and smart speakers. In any audio system that exhibits sound feedback from the loudspeaker to the microphone, acoustic echo cancellation can be applied to remove the unwanted echo from the audio signal. Compared to line echo cancellation, acoustic echo cancellation is much more complex because the number of reflections is greater and the high variability in the echo path of the acoustic environment. A well-designed Acoustic Echo Canceller should be able to be easily integrated into a wide variety of acoustic environments with different levels and types of perceived echo paths and background noise. VOCAL’s AEC and noise control library module can be used in nearly every acoustical environment to achieve to achieve highly intelligible and clear, echo-free communication.
Acoustic Echo Cancellation Features
- Optimized for ANSI C and leading architectures
- ITU G.167 Recommendation compliant
- Rapid convergence
- Fast re-convergence for echo path changes
- Advanced double talk detection with low divergence during double talk
- Non-linear Processing (NLP)
- Built-in Noise Reduction
- Long configurable echo tail length (up to 512ms)
- Configurable narrowband(8kHz), wideband(16kHz), super-wideband(32kHz), fullband(44.1kHz,48kHz), and high-resolution fullband(96kHz) sampling rates
- Automatic echo delay estimation
- Anti-howling control
- Automatic Gain Control
- Stereo and Multiple Mic Modes available
- Comfort Noise Generation (CNG) with noise matching feature
- Portable, re-entrant and re-locatable library code
- Supports user callable functions
AEC Operational Characteristics
- Fast Convergence*: ERLE = 30dB in 1s
- Low Steady-State Mis-adjustment*: ERLE > 50 dB
- Double Talk Detector, cancellation during doubletalk
- Nonlinear Processing: Residual Echo < -60dB
- Noise Reduction: SNR Improvement > 15dB
*Note: These numbers reflected the capability of our implementation under constant excitation in a time-invariant environment.
AEC Design Constraints
- The standard VOCAL echo canceller API operates on 16-bit signed input values, and returns 16-bit signed values. (32-bit API for 24-bit sample data is available upon request).
- A variable internal excitation delay is available to provide full echo canceller tail length in the presence of known system latencies.
- Performance of echo cancellation is highly dependent on the device under test and its acoustic environment. The amount and speed of convergence is dependent on the level of linearity of the echo path and the level of the background noise.
- Large numbers of echo canceller control values are available to modify the behavior of the canceller should needs dictate, however doing so is not recommended.
AEC Operational Performance
Target sample rates: 8kHz to 96kHz
Bit Depths Supported: 16-bit, 24-bit
Echo tail length: VOCAL’s Acoustic Echo Canceller echo span coverage is configurable up to 512 milliseconds. In custom designs, the echo span coverage can exceed 512 milliseconds, if requested.
AEC Functional Description
What is echo cancellation software? The Acoustic Echo Cancellation software is designed for removing/suppressing acoustic reflections of the loudspeaker signal captured by the microphone. Line/network echo cancellation software primarily address echo signals produced by reflections from hybrid circuits (or transformers) converting 4-wire interface into 2-wire interface in POTS/PSTN systems.
Characteristics of the reflected acoustic signals are as follows:
- Relatively long echo span (a.k.a. echo tail), often exceeding 160ms;
- Wider range of echo signal levels, often extending over high signal levels (thus corresponding to low ERL values, reaching negative values in some configurations);
- Frequent changes of echoes (illustrated by variations of echo path impulse responses), according to position of the voice terminal and/or speaker with respect to reflecting objects in the near-end room;
- Due to nonlinear behavior of the loudspeaker, the relationship between the acoustic pressure produced by the loudspeaker and the electrical signal driving it is not exactly linear; therefore, an adaptive filter that, in most designs, is a linear component, cannot adequately model the echo path. As a result, more stringent requirements are imposed onto the NLP so any audible traces of residual echoes are removed.
The above mentioned characteristics of echoes require acoustic echo cancellers be equipped with more advanced adaptive filters, double talk detectors and nonlinear processors than their line/network echo canceller counterparts.
For example, the adaptive filters used in Acoustic Echo Cancellers have to cover well the anticipated echo span; thus their lengths, in milliseconds, have to be at least as long as the echo span. VOCAL Acoustic Echo Canceller’s echo span coverage is configurable and can reach up to 256 milliseconds. In custom designs, the echo span coverage can be made longer than 256 milliseconds, if requested.
How do I cancel acoustic echo? To cancel acoustic echo, at minimum you need the loudspeaker signal, the microphone signal, and an adaptive filter, such as the normalized least means squares. VOCAL’s Robust Acoustic Echo Canceller uses a block NLMS algorithm, performed in the sub-band domain, providing a short convergence time. Echo cancellation is performed independently on each sub-band.
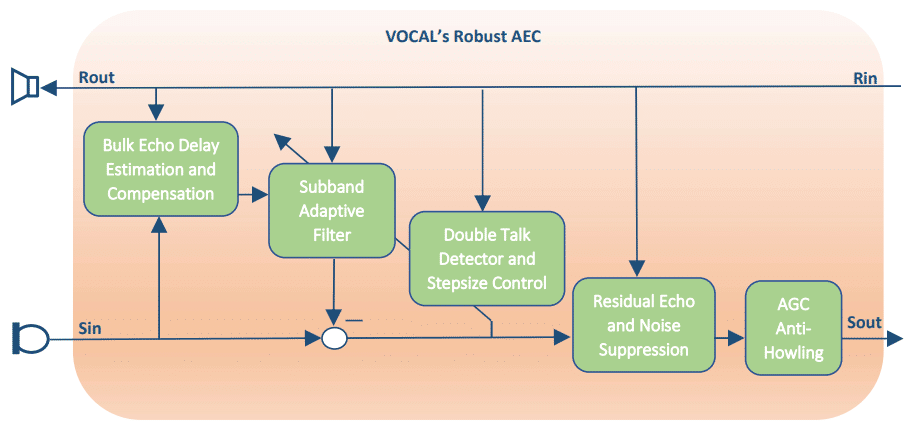
The figure below shows the basic building blocks of an acoustic echo cancellation solution. In our implementation, the Rin / Rout is considered to be the signal that is transmitted by the loudspeaker; this is the excitation signal. The signal received by the microphone is considered Sin, and Sout is the echo cancelled, noise reduced result. The transmitted signal from the far-end user, Rin, is used in the following blocks: bulk echo delay estimation, subband adaptive filter, residual echo suppression (NLP), and double talk detection (DTD). The received signal from the microphone, Sin, containing the echo signal and near-end talk is used by the bulk echo delay estimation. The Sin signal is then subtracted by the estimated echo signal from the subband adaptive filter to produce the system identification error signal. This signal is used to update the echo canceller filter, double-talk detector, variable step size control and is processed by the residual echo suppressor and the noise reduction block. Finally, the result is processed through optional features, such as AGC and anti-howling.
Acoustic Echo Cancellers are expected to address (cancel/suppress) echoes of large energy, comparable or exceeding the equivalent energy of the incoming signals. Such conditions pose challenging requirements for double-talk detectors. An advanced VOCAL Acoustic Echo Canceller’s double-talk detector performs well in conditions where ERL > -6dB.
Adaptive filters of AECs have to react rapidly to echo path changes. VOCAL Acoustic Echo Canceller incorporates a subband adaptive filter whose adaptation speed is superior when compared with competitive solutions, while its adaptation depth is more than adequate.
For systems with high levels of non-linearities, our solution also provides a non-linear processing option to remove any residual echo leftover from adaptive filtering. The amount of suppression of residual echo is dependent on the current state of the system. VOCAL’s AEC SDK incorporates an advanced NLP which adequately removes traces of residual echoes.
Many environments contain high levels of background noise that can be prohibitive to effective communications. VOCAL’s acoustic echo canceller software includes a noise reduction option to further improve the signal-to-noise ratio of audio signals and voice intelligibility, for both stationary and non-stationary noise. This is achieved by utilizing spectral subtraction via noise estimation and also the sound masking properties of the human ear to provide clear communication. VOCAL’s solution is a complete echo cancellation and noise reduction (ECNR) software package.
Since signal gains are controllable by the end user (by adjusting volume knobs for the loudspeaker or for the microphone, and that affects the total system loop gain), Acoustic Echo Cancellers, being a part of the closed-loop system, can be potentially exposed to system instability, which, if not controllable, may manifest as a howling effect. VOCAL’s Acoustic Echo Canceller software is equipped with an anti-howling feature that minimizes the howling effect.
Acoustic Echo Cancellation Standards Compliance: A Brief Note
In general, acoustic echo canceller performance requirements are driven by “industry standards” and customer requirements.
In the area of telephony applications, there is ITU-T G.167 standard (a.k.a. Recommendations) that outlines specific performance requirements. However, the standard has become defunct. Thus, formally, it is no longer considered as being normative and governing the AEC product performance. Yet, it is still being frequently quoted and referenced. It is worth mentioning that a G.167-compliant AEC does not necessarily meet ITU-T G.168 standard, despite the fact that requirements related to adaptation speed and echo path coverage for AEC are more demanding for AEC than for LEC/NEC.
Other applicable standards include ITU-T G.160, ITU-T P.340, P.1100, P.1110, Microsoft Teams, 3GPP, IEEE and other related documents. VOCAL’s engineering team will support their customers during the product compliance and certification testing process. VOCAL’s engineering team has performance a number of proprietary tests to ensure the solution is as robust as possible.
More Information on Acoustic Echo Cancellation
- Echo Cancellation Overview
- Echo Canceller Design
- Stereo Acoustic Echo Cancellers
- Sub-Band Acoustic Echo Cancellation
- Combined Line and Acoustic Echo Canceller
- Acoustic Echo Canceller and Noise Reduction Combined
- Challenges of Wideband Acoustic Echo Cancellation
- Acoustic Echo Diagnostics
Platforms
VOCAL’s optimized Echo Cancellation software is available for the following platforms. Please contact us for your specific Echo Cancellation application platform requirement.
| Processors | Operating Systems |
| · Texas Instruments – C6000 (TMS320C62x, TMS320C64x, TMS320C645x, TMS320C66x, TMS320C67x), DaVinci, OMAP, C5000 (TMS320C55x) · Analog Devices – Blackfin, TigerSHARC, SHARC · PowerPC · MIPS – MIPS32, MIPS64, MIPS4Kc · ARM – ARM7, ARM9, ARM9E, ARM10E, ARM11, StrongARM, ARMCortex-A8/A9/A15/A3x/A5x/A7x, Cortex-M3/M4/M7/M33 · Intel / AMD – x86, x64 (both 32 and 64 bit modes) | · Google Android · Apple iOS / iPhone / iPad & MacOS · Unix, Linux, μClinux, BSD · Microsoft Windows ACM / RTC / CE / Mobile · Symbian · eCOS / eCOSPro · Wind River VxWorks · Green Hills Integrity · VOCAL LANsEND · Micrium μCOS |