The first go-to algorithm for acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) is a the gradient descent least mean squared (LMS) algorithm. The LMS algorithm however has a challenge in the convergence time making it not quite suitable for real time operating system which require fast convergence of the algorithm with low computation time. An adaptation of the LMS algorithm, the normalized LMS algorithm is used to mitigate this challenge. Consider the LMS algorithm which proceeds as:
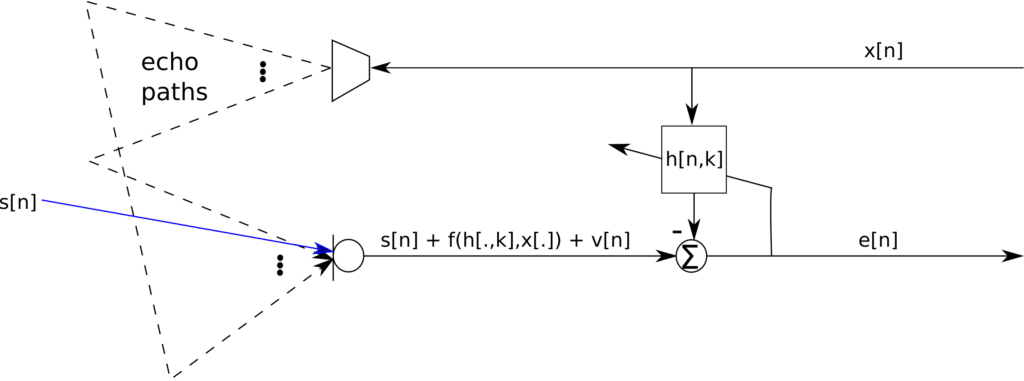
Figure 1: Single line AEC architecture
where are the filter taps being estimated,
,
is additive noise and
is the descent parameter. The NLMS seeks to optimize the choice of the value of
used. The square of the error signal, given as
is minimized for the optimal value such that the constraint
. A new cost function thus arises, given by
which leads to
Further, the partials with respect to the Lagrange multipliers are
Thus the complete solution will proceed as:
The NLMS update equation looks similar to the original LMS update equation with . In most cases, a small constant
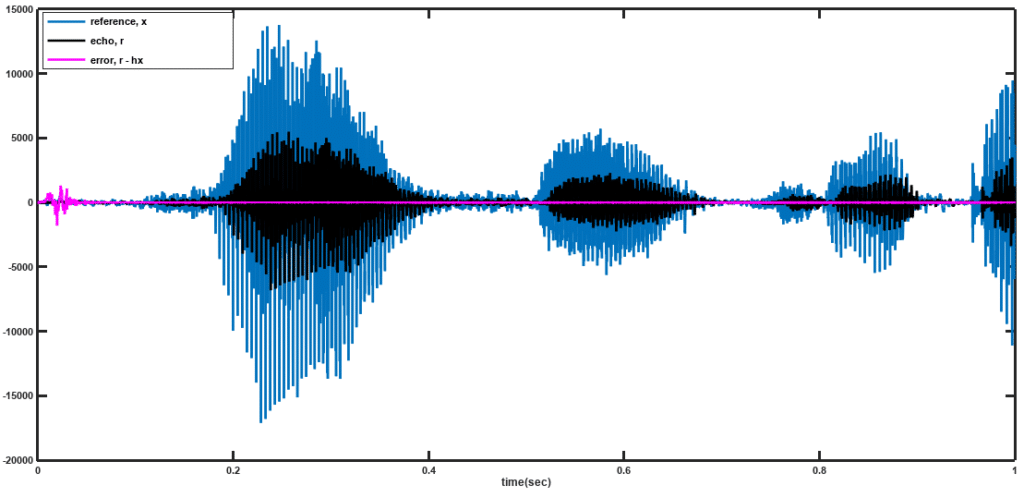
is included for a more graceful descent of the algorithm and also to satisfy the Wolfe conditions. A sample result for this algorithm is shown in Figure 2 below.
Figure 2: Performance of NLMS AEC
VOCAL Technologies offers custom designed solutions for beamforming with a robust voice activity detector, acoustic echo cancellation and noise suppression. Our custom implementations of such systems are meant to deliver optimum performance for your specific beamforming task. Contact us today to discuss your solution!