Video streaming technology is one way to deliver video over the Internet. Using streaming technologies, the delivery of audio and video over the Internet can reach many millions of customer using their personal computers, PDAs, mobile smartphones or other streaming devices. The reasons for video streaming technology growth are:
- broadband networks are being deployed
- video and audio compression techniques are more efficient
- quality and variety of audio and video services over internet are increasing
There are two major ways for the transmission of video/audio information over the Internet:
Download mode. The content file is completely downloaded and then played. This mode requires long downloading time for the whole content file and requires hard disk space.
Streaming mode. The content file is not required to be downloaded completely and it is playing while parts of the content are being received and decoded.
A Streaming media player can be either an integral part of a browser, a plug-in, a separate program, or a dedicated device, such as Apple TV, Roku Player, iPod, etc. Video files may also include embedded players.
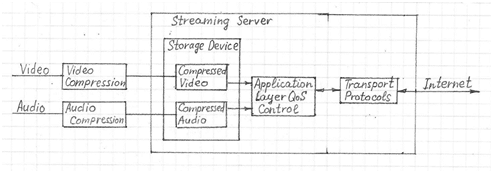
There are two types of streaming video content distribution: on-demand and programmed-time streaming. In on-demand distribution the viewer is able to choose what content to play at any time. This type of streaming raises bandwidth costs since it is necessary to establish a new network stream for each player. Programmed-time streaming establishes a channel for an audience on a scheduled basis
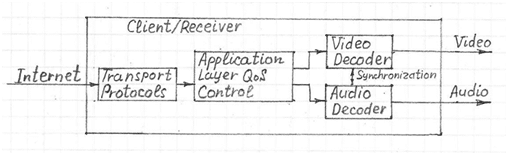
Real-time streaming video applications require media packets to arrive in a timely manner. Excessively delayed packets are useless and are treated as lost. Streaming technology also assumes that some packets may be discarded, to meet time and/or bandwidth constraints. The User connection can be adapted to available user bandwidth.
For streaming technology UDP/IP (User Datagram Protocol) is used which delivers the multi-media flow as a sequence of small packets. The application layer protocol is RTP/RTSP (Real-time Transport Protocol /Real Time Streaming Protocol) which is implemented on top of UDP/IP to provide an end-to-end network transport for video streaming. MMS(Microsoft Media Server) is also utilized for video streaming.
The video stream is compressed using a video codec such as H.264 or VP8. The audio stream is compressed using an audio codec such as MP3, Vorbis or AAC. Encoded audio and video streams are assembled in a container bitstream such as MP4, FLV, WebM, ASF or ISMA.